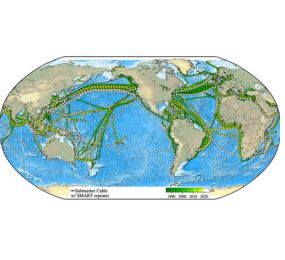
The internet connects billions of people across continents every second, and what makes this global communication possible is a vast network of submarine cables. These undersea fiber-optic cables are the backbone of our digital world, carrying over 95% of international data traffic.
But what happens when one of these cables is damaged?
In this post, we’ll take a closer look at submarine cable damage and repair, what causes these issues, how they’re fixed, and what claims and remedial measures are in place in 2025 to handle such incidents.
What Is Submarine Cable Damage?
Submarine cable damage refers to any physical harm or functional failure in undersea communication cables. These cables are laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across oceans and seas.
In 2025, there are over 1.5 million kilometers of submarine cables globally. Though these cables are engineered to withstand natural and human-made threats, they are not invincible.
Common Causes of Submarine Cable Damage
More than 150 cable faults are reported annually worldwide. The most common reasons for submarine cable damage include:
- Fishing and Anchoring: These account for nearly 70% of cable damages. Fishing trawlers and ship anchors accidentally drag or cut cables lying on the seabed.
- Natural Events: Underwater earthquakes, landslides, and strong ocean currents can stress or break cables.
- Deliberate Sabotage: While rare, there are occasional incidents of intentional damage due to geopolitical conflicts or criminal intent.
- Shoreline Erosion and Construction: Activities near coastal areas can disturb shallow cable landings.
How Is Submarine Cable Repair Done?
Submarine cable damage and repair is a highly coordinated and technical process. It involves several steps and specialized equipment:
1. Damage Detection
- Network monitoring systems detect loss of signal or connectivity.
- Survey ships use sonar and underwater drones to locate the damage.
2. Cable Retrieval
- Specialized cable ships are deployed to the damaged area.
- Grapnels (underwater hooks) are used to lift the cable to the surface.
3. Repair Operation
- Technicians splice the damaged section with a new segment onboard the ship.
- The repaired cable is tested for signal quality before being lowered back to the seabed.
4. Post-Repair Testing
- Once in place, end-to-end testing ensures the system is back online with minimal latency or packet loss.
On average, it takes about 10 to 20 days to fully repair a submarine cable, depending on weather, location, and accessibility.
Claims and Legal Measures
Because submarine cable damage and repair affects not just businesses but national infrastructures, proper legal protocols and claims processes are essential.
Claim Protocols in 2025
- Ownership Claims: Most submarine cables are owned by consortiums of telecom providers. Any damages usually result in joint claims to insurance companies.
- Third-Party Liability: If a vessel or company is found responsible, they may be liable for millions in damages and loss of service penalties.
- Marine Insurance: Submarine cable operators maintain comprehensive insurance that covers accidental and natural damages.
Regulatory Oversight
- The International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC) continues to play a key role in setting repair and protection standards.
- Many countries now mandate Submarine Cable Protection Zones (SCPZs) where fishing and anchoring are restricted.
Remedial Measures in Place
Preventing cable damage is more cost-effective than repairs. In 2025, there are several proactive measures being implemented:
- Real-Time Ship Tracking: Submarine cable maps are integrated with global maritime tracking systems to alert ships if they enter a restricted zone.
- Cable Burial: Cables are buried deeper (up to 3 meters in certain zones) using plows and ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles).
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Coastal communities and fishing industries are educated on the importance of undersea cables.
- Advanced Cable Materials: The latest generation of cables is reinforced with aramid yarn and improved sheathing to withstand greater pressure and stress.
Why This Matters in 2025
With the increasing demand for low-latency services like 5G, cloud computing, and AI-driven systems, the importance of uninterrupted international connectivity is critical. Submarine cable damage and repair is not just a technical challenge—it’s an economic and security issue.
An unplanned outage can cost cloud providers, financial institutions, and governments millions of dollars per hour. Having swift and structured repair protocols, supported by legal frameworks and insurance, is essential.
Key Statistics
- 95% of global data is carried by submarine cables.
- Over 150 cable faults occur annually.
- Fishing activities account for 40-50% of all damages.
- Average repair time: 10–20 days.
- Cable ships: About 60 globally, operating on-call to repair damages.
FAQs
Q1: How long do submarine cables last?
Answer: Typically, submarine cables have a lifespan of 20–25 years, but upgrades or damages may require earlier replacement.
Q2: Who pays for cable repair?
Answer: Costs are usually shared by the owning consortium, or covered by insurance if damage is accidental. If negligence is proven, the responsible party may bear the full cost.
Q3: Are there backup systems?
Answer: Yes, most data is rerouted through alternate cable paths to prevent total outages. However, this can result in slower speeds and reduced bandwidth temporarily.
Q4: Can submarine cables be hacked?
Answer: While rare, it’s technically possible. Hence, encryption and cable route security are major concerns for cable operators and governments.
Final Thoughts
As our world becomes more connected, protecting the arteries of our digital ecosystem is a global priority. Understanding submarine cable damage and repair helps underline just how fragile and vital these systems are. Whether you're a tech professional, business owner, or curious reader, staying informed helps appreciate the unseen yet critical infrastructure we all rely on daily.